Vector Database and Embeddings: Key Points and Subpoints
1. What is a Vector Database?
A vector database is a specialized type of database designed to store and manage data in vectorized form. It is particularly useful for high-dimensional and complex data like text, images, audio, and video.
1.1. Definition and Purpose
- Stores data in numerical form (vectors).
- Enables efficient storage, retrieval, and search of complex data.
- Uses mathematical techniques to compare, cluster, and analyze data.

1.2. Structure of Vectors in a Vector Database
- A vector is an array of numbers, where each number represents a specific characteristic of the data.
- Each dimension of a vector captures a different feature of the data object.
- Example: A vector representing an image might include:
- Pixel intensity
- Color channels (RGB)
- Texture features
- Spatial location
1.3. Advantages of Vector Databases
- Efficient handling of heterogeneous data (text, images, audio, video, etc.).
- Enables similarity-based searches, crucial for AI and ML applications.
- Optimized for high-dimensional data, which traditional relational databases struggle with.
2. What are Vector Embeddings?
2.1. Definition of Embeddings
- A vector is just an array of numbers, but when these numbers encode meaningful information about data (structure, properties, semantics, etc.), it is called a vector embedding.
2.2. Purpose of Embeddings
- Embeddings help convert unstructured data into a numerical format that a computer can understand.
- They capture semantic relationships between objects.
- Used in AI, machine learning, and deep learning models for processing complex data.
2.3. Examples of Embeddings
- Word embeddings: Captures meaning and context of words.
- Image embeddings: Captures texture, color, and object details.
- Video embeddings: Captures motion, object tracking, and scenes.
- Audio embeddings: Captures pitch, frequency, and tone.
3. How are Embeddings Generated?
3.1. Embedding Models
-
Machine learning models convert raw data (text, image, video, etc.) into numerical representations.
-
Different embedding models are used for different data types.
-
Examples:
- Word2Vec, GloVe (for text embeddings).
- ResNet, VGG, CLIP (for image embeddings).
- MFCC, Wav2Vec (for audio embeddings).
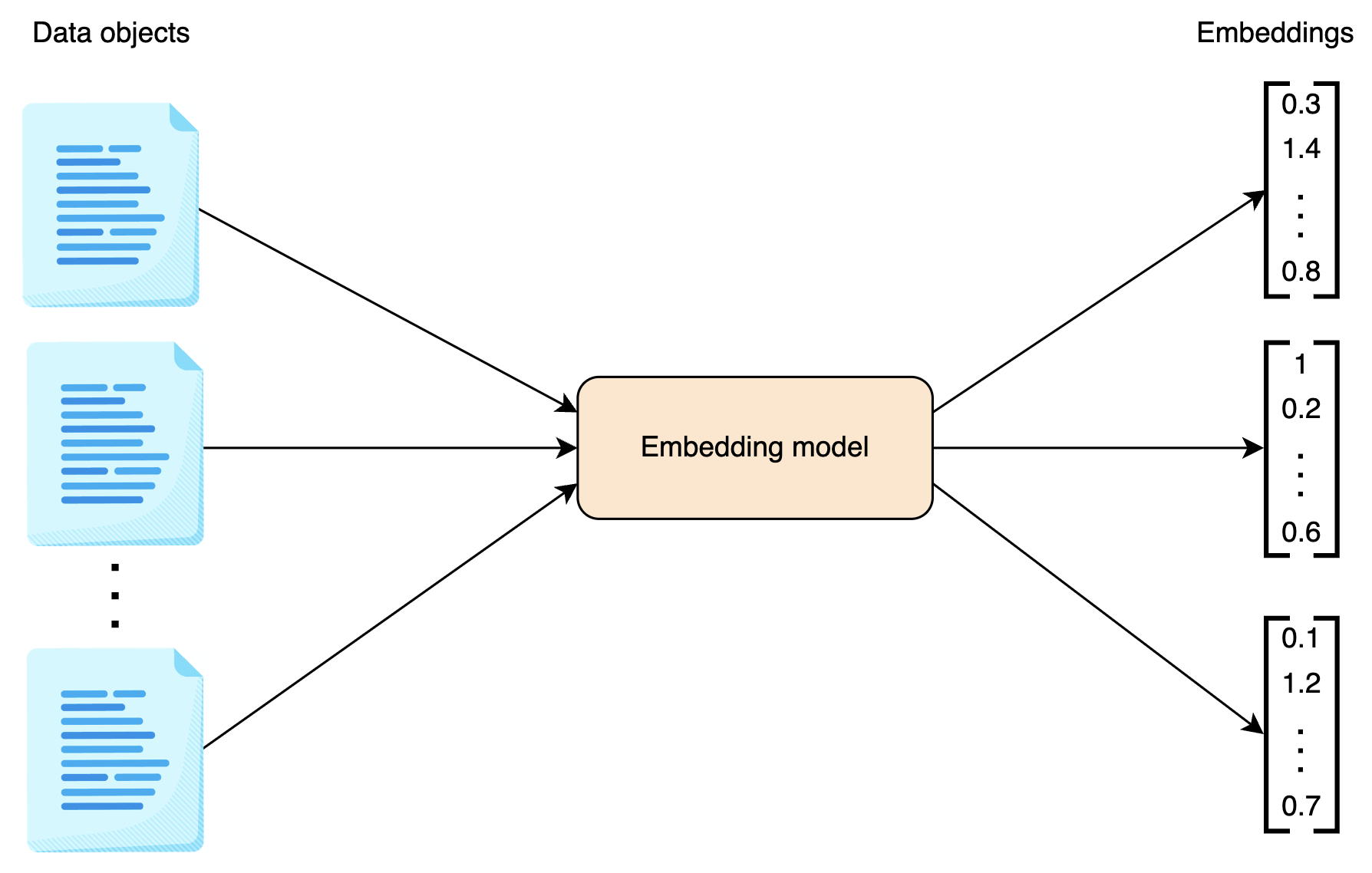
3.2. Process of Generating Embeddings
- Input Data → Raw data (text, image, video, etc.).
- Pass through an Embedding Model → Converts it into a numerical vector.
- Output → High-dimensional embedding vector representing the essential features of the input.
4. Relationship Between Vector Databases and Embeddings
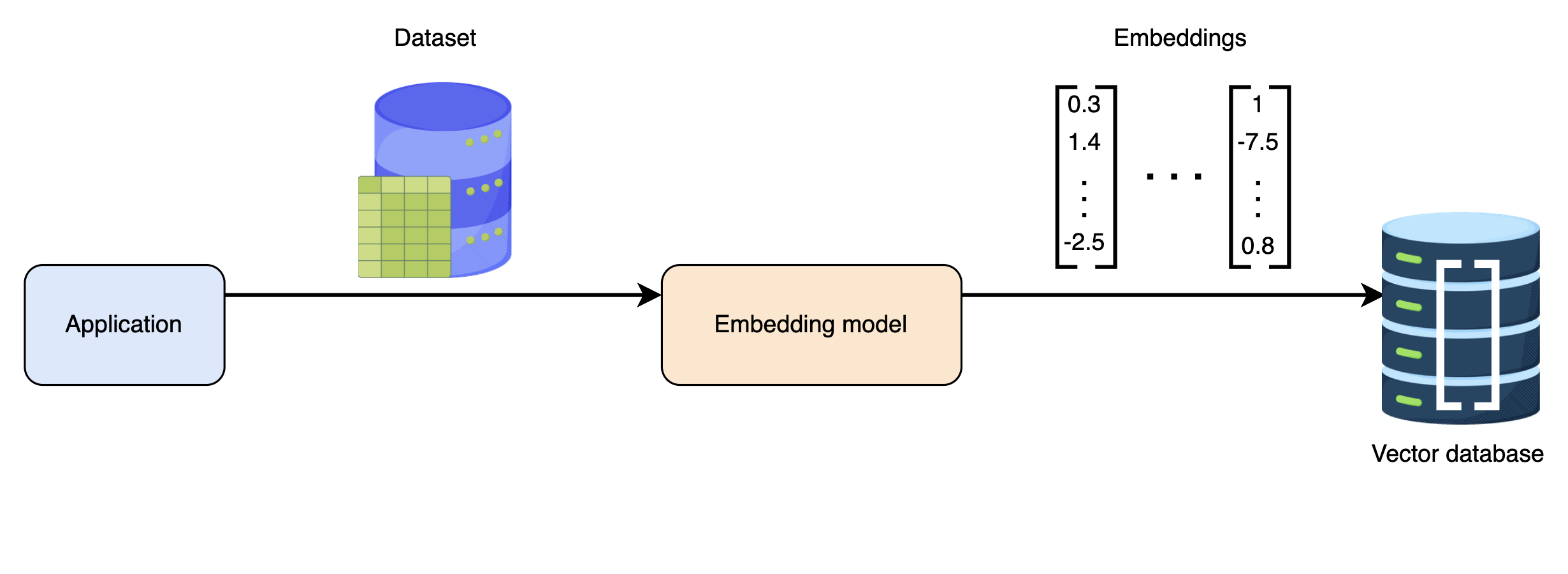
4.1. Role of Vector Databases in Embedding Management
- A vector database acts as a repository for embeddings.
- It enables efficient indexing, searching, and retrieval of embeddings.
4.2. Importance in AI and ML Applications
- Similarity search
- Recommendation systems
- Clustering and classification
- Anomaly detection
5. How Vector Databases Perform Similarity Search?
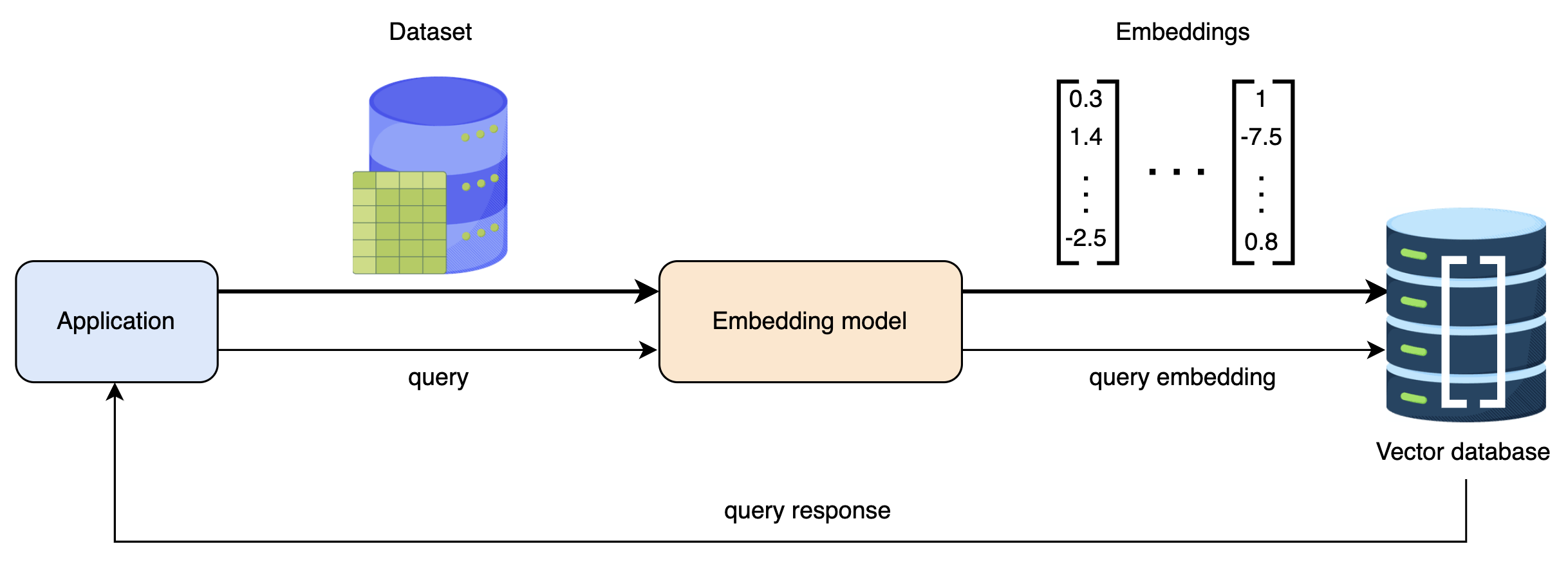
5.1. Steps to Find Similar Images Using a Vector Database
Step 1: Generate Embeddings
- Images are fed into an image embedding model (e.g., ResNet, CLIP).
- The model outputs a high-dimensional vector for each image.
Step 2: Store Embeddings
- The embedding vectors are stored in the vector database.
- The database indexes them efficiently for quick retrieval.
Step 3: Query Processing
- A user submits a query image.
- The query image is converted into an embedding using the same model.
Step 4: Similarity Search
- The vector database compares the query embedding with stored embeddings.
- Similarity is measured using mathematical distance metrics, such as:
- Euclidean distance
- Cosine similarity
- Manhattan distance
Step 5: Return Results
- The database retrieves the most similar images based on vector similarity.
- These similar images are sent back as search results.
6. Real-World Applications of Vector Databases
6.1. Image and Video Search
- Google Reverse Image Search uses embeddings to find similar images.
6.2. Recommendation Systems
- YouTube, Netflix, and Spotify use embeddings to recommend videos, movies, and songs.
6.3. Facial Recognition
- Security systems compare facial embeddings for authentication.
6.4. NLP and Chatbots
- Language models use text embeddings for understanding context and meaning.
6.5. Fraud Detection and Anomaly Detection
- Embeddings help detect unusual transactions in banking.
7. Summary
- Vector databases store and manage embeddings for complex data types.
- Embeddings represent meaningful numerical representations of data objects.
- Vector databases enable similarity search, recommendation, and clustering.
- They use embedding models (e.g., Word2Vec, ResNet) to generate numerical vectors.
- Similarity searches use distance metrics (Euclidean, cosine similarity) to find related objects.
Note: This article is inspired by the concepts learned from the Educative course Vector Database.